POMEGRANATE - DISEASE MANAGEMENT
Disease Management & Diagnosis

Leaf and Fruit spot
(Pseudocercospora puniceae (Henn.) Deighton)
Symptoms:
This is a very serious disease of pomegranate plants affecting leaf and fruits. Pathogen causes irregular, scattered, yellowish spots on leaves having a halo around at the early stage, subsequently the spots increase in size and form bigger patches and become blackish. The lesions are covered with dull white crust of fungal growth. Severe infection of the disease leads to defoliation and hampers plant growth. On flower buds brownish black irregular small spots appear which grow in size along with the fruit. Spots become deeper and more prominent. At greenish stage of fruit, reddish irregular dots/spots develop on the fruits. The spots get covered with deposit of ash colored spores under favorable humid conditions. Mature fruits show numerous black, irregular, slightly corky patches of the infected hard necrotic tissue. Severely infected fruits show cracking at times. Disease is severe in high humidity areas and during rainy season.
Managemnt :
Hexaconazole (Contaf 0.1%) or carbendazim (Bavistin 0.1%) or thiophanate methyl (Topsin M or Roko 0.1%) sprayings control the disease. First spray at flower bud stage and subsequently 8-9 sprays at 7-10 days interval depending upon the weather conditions. Among non-systemic fungicide Chlorothalonil (Kavach 0.2%) or Mancozeb (Indofil Dithane M 45 0.2%) also check the disease.

Leaf and Fruit spot
(Pseudocercospora puniceae (Henn.) Deighton)
Symptoms:
This is a very serious disease of pomegranate plants affecting leaf and fruits. Pathogen causes irregular, scattered, yellowish spots on leaves having a halo around at the early stage, subsequently the spots increase in size and form bigger patches and become blackish. The lesions are covered with dull white crust of fungal growth. Severe infection of the disease leads to defoliation and hampers plant growth. On flower buds brownish black irregular small spots appear which grow in size along with the fruit. Spots become deeper and more prominent. At greenish stage of fruit, reddish irregular dots/spots develop on the fruits. The spots get covered with deposit of ash colored spores under favorable humid conditions. Mature fruits show numerous black, irregular, slightly corky patches of the infected hard necrotic tissue. Severely infected fruits show cracking at times. Disease is severe in high humidity areas and during rainy season.
Managemnt :
Hexaconazole (Contaf 0.1%) or carbendazim (Bavistin 0.1%) or thiophanate methyl (Topsin M or Roko 0.1%) sprayings control the disease. First spray at flower bud stage and subsequently 8-9 sprays at 7-10 days interval depending upon the weather conditions. Among non-systemic fungicide Chlorothalonil (Kavach 0.2%) or Mancozeb (Indofil Dithane M 45 0.2%) also check the disease.

Anthracnose
(Colletrotrichum gloeosporioides (Penz.) Penz.&Sacc)
Symptoms:
The disease manifest in various form of symptoms causing leaf blight, fruit spot, wither tip, die back and fruit rotting as described below:
(i) Leaf blight: The disease starts as minute, dull violet black or black spots surrounded by yellow necrotic areas. The spots enlarge; coalesce to form depressed large spots of aniline black in color. Severely infected leaves show necrotic areas extending from leaf margins to cover whole leaf blade. Leaves show curling at some points and severely infected leaves, become dry and fall off. Sometimes shot hole stage is also observed.
(ii) Fruit spots: The pomegranate fruits are highly susceptible to attack by this pathogen from early stages of development (flower bud stage - (Reddish) and fruit enlargement stage before attaining greenish color and subsequently at color breaking stage. Smaller brownish spots, which become depressed subsequently, increase in size to form the large spots. During greenish stage of fruit development infection remains quiescent and exhibit symptoms at color breaking stage. Mature fruits show numerous brownish black depressed spots, which coalesced to form bigger patch. The entire infected portion changes color to yellowish brown and fruits start rotting which becomes serious during storage. Severe infection of fruits results in flower bud and fruit drop and in mummified fruit and at times cause rupture of the fruit exocarp also.
(iii) Wither tip and die back: Younger, developing shoot tips are killed due to attack of pathogen and some developing branches show drying from the tips backward with necrotic areas extending downwards, such branches become dry and devoid of foliage subsequently and give die back appearance. These symptoms are more pronounced in older trees and neglected orchards.
Managemnt :
For the disease management, prune the dried twigs and branches and burn them. After pruning a general spray of copper oxychloride (Blitox 0.3%) and pasting of cut ends with copper fungicide should be practiced. Subsequently spraying with hexaconazole (Contaf 0.1%) or carbendazim (Bavistin 0.1%) or thiophanate methyl (Topsin M or Roko 0.1%) should be given. First spray at flower bud stage and subsequently 5 – 6 sprays at the interval of 7-10 days interval have to be provided. Chlorothalonil (Kavach 0.2%) or mancozeb (IndofilDithane M 0.2%) in non-systemic category also control the disease.
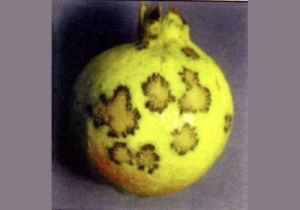
Alternaria leaf spot and fruit rot
(Alternaria alternata (Fr.) Keissl)
Symptoms:
Minute pale brown to reddish brown circular to irregular spots develop on the ventral surface of the leaves. The spots, enlarge coalesce to form bigger spots, dark brown in colour having concentric rings. Within a few days of infection by pathogen, leaf brightening becomes more prominent and such affected pale yellow leaves dry and fall down.
On fruits, the pathogen causes both external as well as internal rotting. Initially minute brown colored spots circular to irregular in outline confined to rind appear on the fruits. As the disease advances the spots turn reddish brown and later on dark brown to black in colour. Fruits lose their natural luster and severe infection of the pathogen leads to internal rotting of fruits, discolouration of central core and the seeds.
Managemnt :
For the disease management, spraying with protectant fungicides namely mancozeb (Dithane M45 0.2%) or zineb (Dithane Z 78 0.2%) or chlorothalonil (Kavach 0.2%) or ziride (Cuman L 0.4%) or with systemic fungicide - iprodione (Rovral 0.2%) should be taken up as the symptoms app

Bacterial Blight
(Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. punicae)
Symptoms:
The symptoms of the disease are noticed on fruits, leaves, branches and stems. On fruits, circular brown to black lesions develop with L or Y or star shaped crack. In advanced stage entire fruit was covered by the lesions, which leads to cracking of the fruits. On leaves water soaked pin head size lesions with yellow halo appear. In advanced stage, the spot enlarge covering entire lamina. Defoliation of infected leaves is noticed in severely affected orchards. On the node, brown to black water soaked elliptical lesions near the auxiliary bud covering entire node is seen resulting into nodal blight. In the advanced stage of nodal infection, affected areas become flattened and depressed with raised edges. Cracking of nodes will lead to death of branches from the infected portion. For the management of the disease,
Management :
For the management of the disease,
• Clean cultivation and orchard sanitation has been advised to prevent the disease.
• Strict quarantine measures have to be followed and infected cuttings should not be supplied or imported.
• Remove the affected fruits, leaves and twigs and destroy by burning them far away from the main field.
• Spray antibiotics, viz. Streptocycline or Bacterinol-100 @ 500ppm and Copper oxychloride (0.3%) two to three sprays at ten day interval followed by one application of Bordeaux mixture (1%).
Prune severely affected plants up to 12.5cm above ground level. Cover the pruned part with Bordeaux paste.

Wilt
(Ceratocystis fimbriata Ellis & Halts / Fusarium oxysporum)
Symptoms:
In some pomegranate orchards, the few branches start dying back, the foliage turn sickly, dropping down turn yellow and shed off. After some time, the affected branches become dry and dead. In severe form the whole mature tree dies all of a sudden even when bearing fruits. When affected tree is cut in length, dark greyish-brown color of wood is visible.
Management :
For the management of the disease, orchards should be kept clean and managed scientifically with proper plant care approach. Branches showing die back symptoms and dried ones should be pruned and destroyed. Soil drenching with benomyl (Benlate 0.1%) or carbendazim (Carbendazim 0.1%) or propiconazole (Tilt 0.1%) should be practiced in plants showing symptoms and nearby apparently healthy plants also.
